Research positions (both PhD and postdoctoral) available in our research group! If you are intrigued by the kind of research we do, please consider applying. [ More Information ]
JOIN US
Announcements
Our paper "Factorized Representations of Query
Results: Size Bounds and Readability" (by Dan Olteanu and Jakub Závodný) received the ICDT 2022 Test of
Time Award. This award recognizes a paper presented 10 years prior at the ICDT conference that has
best met the "test of time" and had the highest impact in terms of research, methodology, conceptual
contribution, or transfer to practice over the past decade.
News: St Cross College,
University of Oxford; Department of Computer
Science, University of Oxford
Maximilian Schleich was Highly Commended in the competition for the CPHC/BCS 2020 Distinguished Dissertation Award. Each year, BCS and the Conference of Professors and Heads of Computing (CPHC) award the best UK PhD/DPhil dissertations in computer science that stand out for their excellence.
Maximilian Schleich received an Honourable Mention for the 2021 SIGMOD Jim Gray Doctoral Dissertation Award for his DPhil dissertation entitled "Structure-Aware Learning over Multi-Relational Databases". The award recognizes excellent research by doctoral candidates in the database field.
LMFAO (Layered Multiple Functional Aggregate Optimisation) 1.0 is now released to the public. [ repository ]
The project moved from the University of Oxford to the University of Zurich.
Keynote on machine learning over relational data at VLDB 2020 in September 2020.
FBENCH 1.0 is now released to the public. [ repository ]
FIVM 1.0 is now released to the public. [ repository ]
Our paper entitled Counting Triangles under Updates in Worst-Case Optimal Time received the best paper award at ICDT 2019 .
Keynote on machine learning over relational data at ICDT 2019 in Lisbon in March 2019.
OPEN LECTURES
Efficient Algorithms
This course gives a unifying overview of the latest research in efficient computation over structured data, with applications spanning databases, artificial intelligence and machine learning, algorithms, and linear algebra. Besides their theoretical interest, algorithms overviewed in this course represent a key differentiator for commercial database and relational AI engines and thus essential knowledge for the future data system engineer.
Topics: (1) Unifying language and computation for: databases, constraint satisfaction problems, satisfiability, probabilistic graphical models, linear algebra matrix computation, gradients and cost functions for machine learning; (2) Commutative semirings; (3) Functional Aggregate Queries; (4) Decompositions; (5) Width measures; (6) Solving joins optimally; (7) Worst-case optimal size bounds for joins; (8) Solving SAT; (9) Solving functional aggregate queries; (10) Solving queries under updates.
From Joins to Aggregates and Optimization Problems
The course introduces recent development on solving a host of computational problems in the database. The unifying theme underlying this development is the use of the structure of the problem to avoid redundancy in data representation and computation.
Research Projects ( 26-minute video overview )
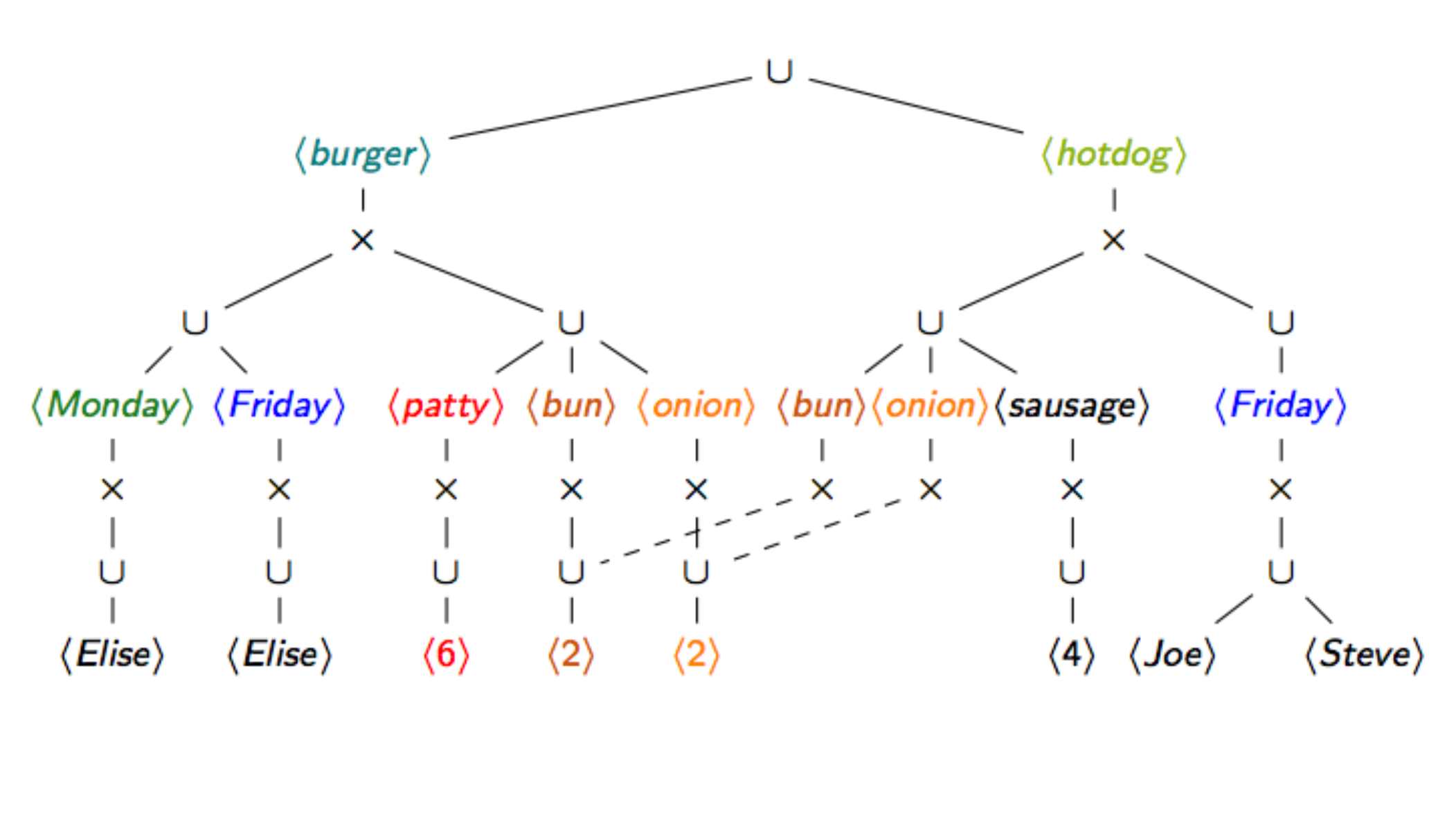
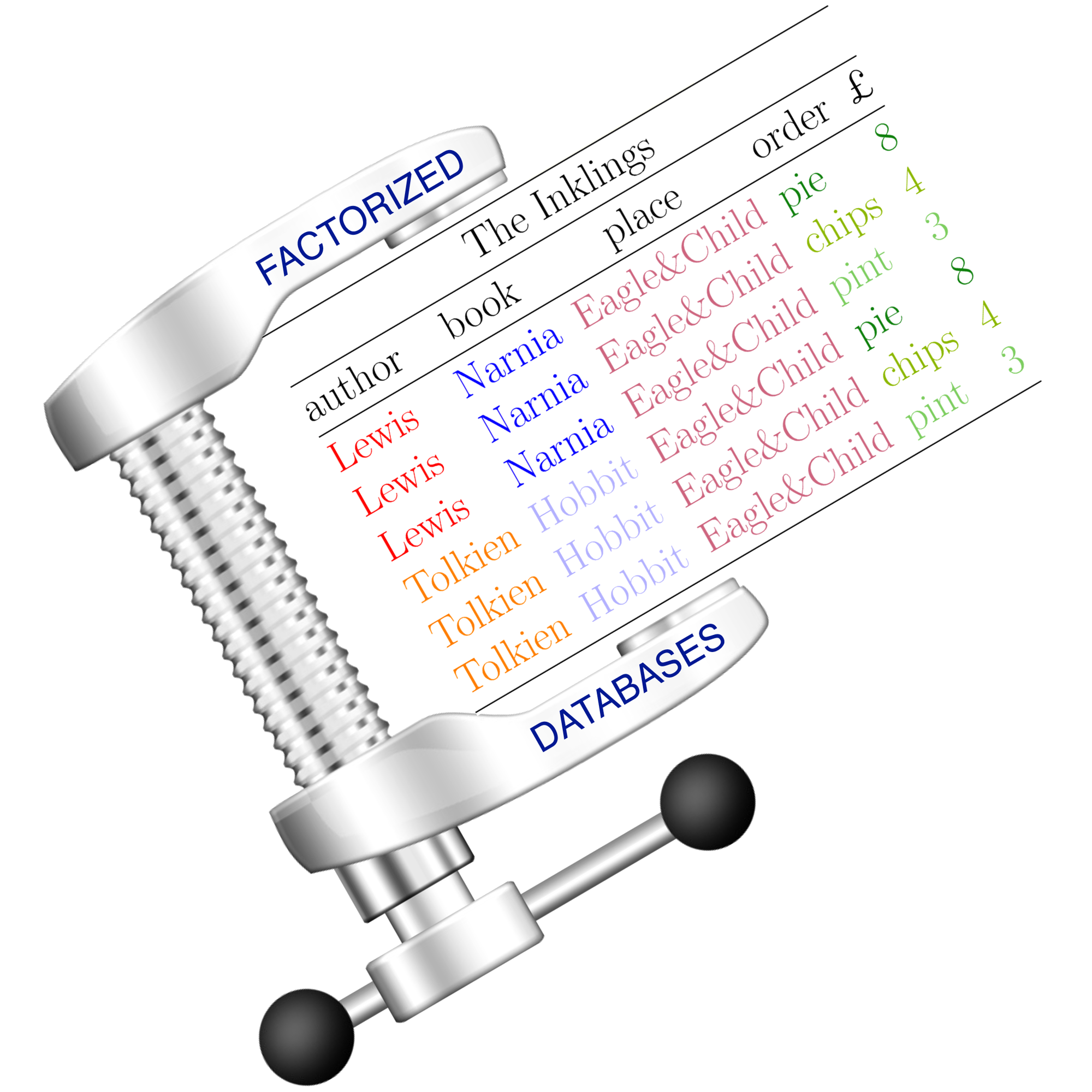
Principles of Factorized Databases
Principled approach to avoiding redundancy in the representation and computation of query results in relational databases. Worst-case optimal computation of compressed, factorized representations for join query results.
Read More..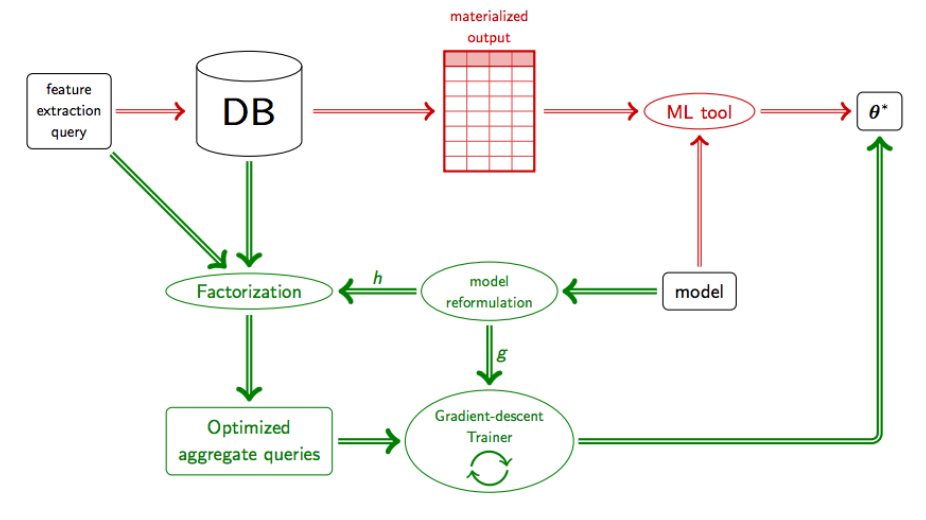
In-Database Analytics
Scalable techniques for machine learning over databases that exploit the relational structure, push the learning task inside the database query engine, and factorise its computation.
Read More..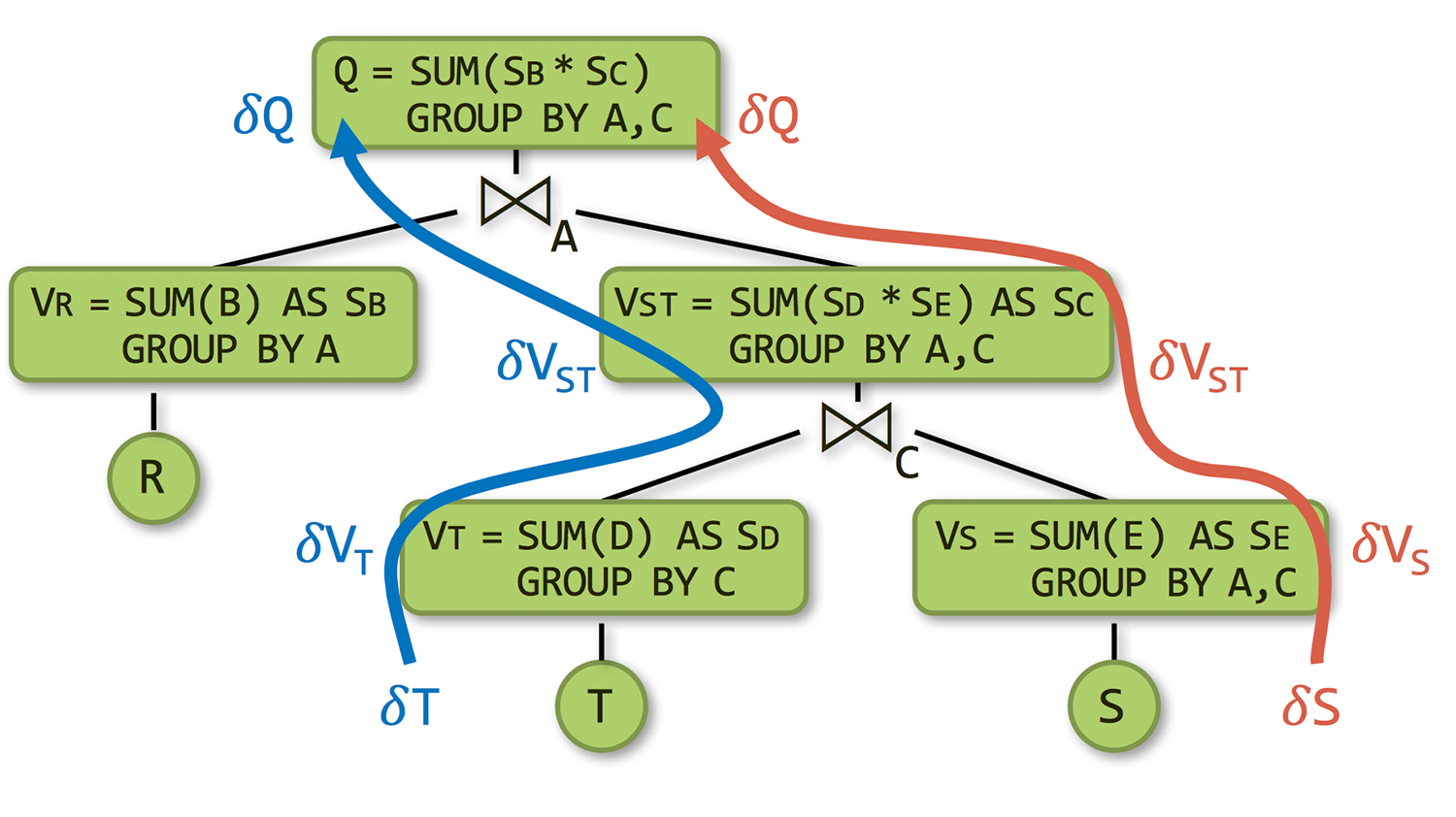
Incremental Maintenance for Analytics
Unified framework for maintaining a wide range of analytics over databases that leverages factorization for underlying queries, output data representation, and bulk updates.
Read More..
The Complexity of Incremental View Maintenance
We investigate trade-offs in static and dynamic evaluation of queries with arbitrary free variables. In the static setting, the trade-off is between the time to partially compute the query result and the delay needed to enumerate its tuples. In the dynamic setting, we additionally consider the time needed to update the query result under single-tuple inserts or deletes to the database.
Read More..